Proof of strength
This proof of static strength is based on the FKM guideline and can be used for sheet metal and welded sheet metal structures, especially when it comes to easily deformable deep-drawn sheets. The calculation process is greatly simplified and is suitable for a rough estimate in optimization loops. For the final calculation, however, it is always recommended to use the original font. 89
| Utilization level | aSK | = |
| Equivalent stress | σV | = | MPa | |||
| Static component strength | σSK | = | MPa | |||
| Overall safety factor | jges | = |
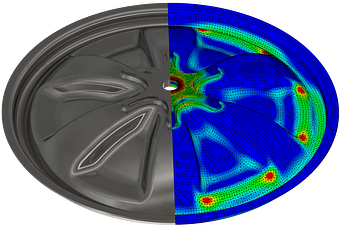
The equivalent stress σV is determined from the FEM according to the shape change hypothesis (von Mises).
The static component strength σSK is the tolerable equivalent stress at the verification point.
The overall safety factor jtot results from the assessment of the damage and the temperature coefficient.
This verification only applies to sheet metal structures made of ductile materials with s0 ≤ 3 mm.
In the case of primarily stressed seams, verification in the weld seam is expressly required. However, such verification is not required for secondary stressed welds (where the force does not pass through the weld) or welds that are only loaded by a stress parallel to the weld.
In structural-mechanical analyzes using the FEM method, singularities often occur that require separate investigation.