Roughness & process selection
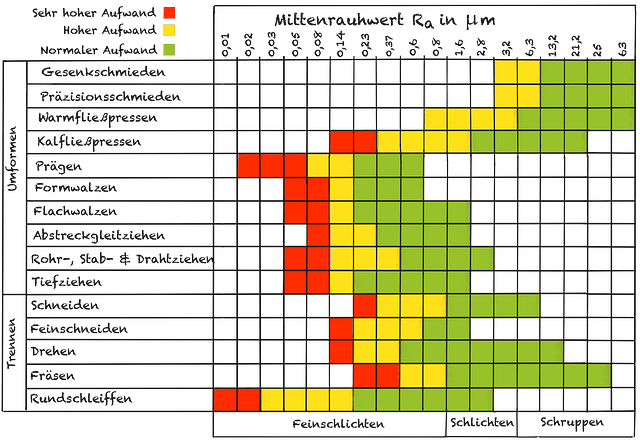
The image shows a matrix that represents different manufacturing processes in relation to their achievable surface roughness Rz. Rz is a measure of the average roughness of a surface, which is very important in manufacturing technology as it can influence the quality and function of a component.
The processes are divided into two main categories: forming and cutting. Forming processes include die forging, precision forging, hot extrusion, cold extrusion, embossing, form rolling, flat rolling, ironing, tube, bar& wiredrawing, and deep drawing. Separating processes include cutting, fine blanking, turning, milling and cylindrical grinding.
The roughness depths Rz are given in micrometers (µm) and range from very fine (less than 1 µm) to relatively coarse surfaces (over 160 µm). The color coding from green to yellow to red indicates the increasing effort that is necessary to achieve certain roughness levels. Green stands for normal effort, yellow for high effort and red for very high effort.
Interestingly, the graphic shows that a finer surface roughness can generally be achieved with forming processes than with cutting processes. This reflects the fact that forming processes allow material to flow rather than remove material, resulting in a smoother surface. In contrast, separating processes remove material, often resulting in a rougher surface. The exception is fineblanking, a cutting process that can achieve surfaces with roughness depths of less than 10 µm, which is due to the high precision of the process.
The data presented is of great importance for engineers and technicians as it allows a quick assessment of the effort and feasibility in relation to surface roughness when selecting manufacturing processes.