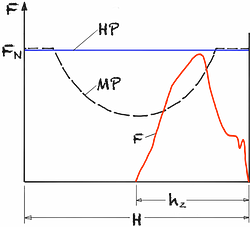
Efficiency of mechanical presses
When deep drawing, power-bound hydraulic or ground-bound mechanical presses are mainly used. In a mechanical press, the force available on the ram varies with the ram travel depending on the kinematics of the drive (e.g. toggle lever or crank drive). In the case of a tied-away press with a standard design, the nominal force of the press FN can only be used for 8% of the total stroke H.3
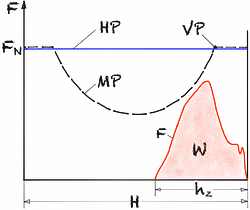
Efficiency continuous stroke ηtot = 0.5... 0.66
The efficiencies depend heavily on the degree of utilization of the machine and the optimal design of the system. The press should be operated at the full utilization point VP.
Mechanical presses are insufficiently designed for deep draws. The bell-shaped curve of the force with deep draws exceeds the force limit curve, which is why hydraulic presses are predominantly used for such applications.