Young's Modulus
The elastic modulus ( young's modulus ) is largely determined by the chemical bonding in the crystal lattice, which is influenced by the melting temperature. The melting temperature of steels varies only slightly, so this results in only small differences in their elastic moduli.
Hot or cold working and certain heat treatments can create textures that can result in significant changes in elastic modulus and poisson's ratio.6
The proportionality constant elastic modulus is defined in the linear-elastic region of the stress-strain diagram until the yield strength Re is reached.
The value corresponds exactly to the stress required to stretch the tensile bar by 100% under the linear-elastic assumption.
The unit is megapascal (MPa) or gigapascal (GPa). You can find values for common sheet metal materials in our material table.
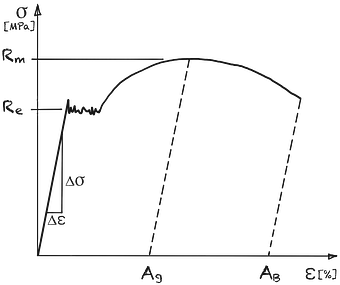
In the stress-strain diagram, the modulus of elasticity corresponds to the slope of the straight line until Re is reached.
The modulus of elasticity has a very dominant influence on the springback of sheet metal. A high modulus of elasticity means low resilience and thus high shape retention.
The modulus of elasticity depends on the temperature and expansion of the material.