Young's modulus & elongation
1.1.2
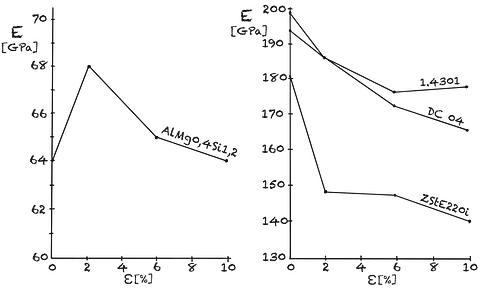
Fig. 1
Dependence of the Young's modulus of elasticity on elongation in different materials
It becomes confusing when the modulus of elasticity depends on the elongation. Tensile tests show a significant decrease in the elastic modulus with increasing plastic deformation. A reduction in the Young's modulus oof up to 20 to 25 percent was determined.7
There are also other research results that could not show any relationship between elongation and young's modulus.
In additional studies it was found that the Young's modulus in steel samples was reduced by around 10 percent at an elongation of 5 percent. After a few days, however, the original Young's modulus returns.
Eqn. 1
| Young's modulus | E | = | GPa |
| Start modulus | E0 | = | GPa | |||
| Elongation | ε | = | % | |||
| Material exponent | m | = |
Calc 1
Young's modulus as a function of plastic elongation*
Material exponent m for steel: -0.06
Material exponent m for aluminum: -0.1
7
Heidl, W. / Rückfederungsverhalten beim Umformen von Feinblechen / EFB Bericht Nr. 109 / … / 1997 / …