Drawing defects
The quality of a deep-drawn component is influenced by various parameters such as blank holder force, friction, forming speed, tool and machine rigidity. If these parameters are not optimally adjusted or coordinated with one another during the deep-drawing process, various defects can occur in the formed component.53937
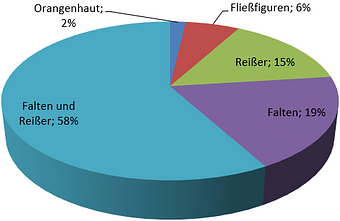
A record of the types of failure that occur when deep-drawing common parts25 shows that the joint occurrence of cracks and creases is the most common type of failure. 35
In the case of parts that are technically demanding in terms of drawing, these errors are also mutually dependent. Due to the control of the material flow, only a low blankholderforce can often be set in some areas of the drawn part, which results in first-order wrinkles. These cannot always be smoothed over the drawing edge and cause the sheet to jam in the clearance. The resulting increased drawing force cannot be transferred by the part, which leads to cracks.
More rarely, only creases or only cracks occur, whereby creases are often tolerated as an additional stiffening element, particularly in the case of body parts that assume a load-bearing function, and therefore do not represent an actual failure.



Factors influencing spring back
The factors affecting spring back are very complex. Here is a rough overview of the primary influencing factors:40
Sheet metal material
- modulus of elasticity
- Yield & yield strength
- Strain hardening exponent
- Anisotropy
- Microstructure (internal friction)
- Surface finish / coating
- Pre-consolidation (for example by drawing beads)
Geometry influences
- Die radius
- Punch corner radius
- clearance
- drawing depth
- Cutting (geometry, size)
- sheet thickness
- Drawn part geometry
Tensile stress
- blankholderforce (course, distribution)
- Cutting (geometry, size)
- Friction (surface, lubrication condition)
- Draw beads (arrangement, penetration depth)
- Die radius
Tribology
- Surface finish (sheet metal & tools)
- Lubricant (type, quantity, distribution)
- Surface pressure
- Forming temperature (external friction)
machine
- Pulling speed
- Tilting between table and ram
- Deflection between table and ram, springback, elasticity (tool/machine)
- Course of ram force over time
- Horizontal offset